Understand More about Gynecologic Cancer
Being diagnosed with a hereditary condition can be scary. That’s why early detection is so important and can make all the difference in the world when it comes to getting in front of a disease.
Know The Basics
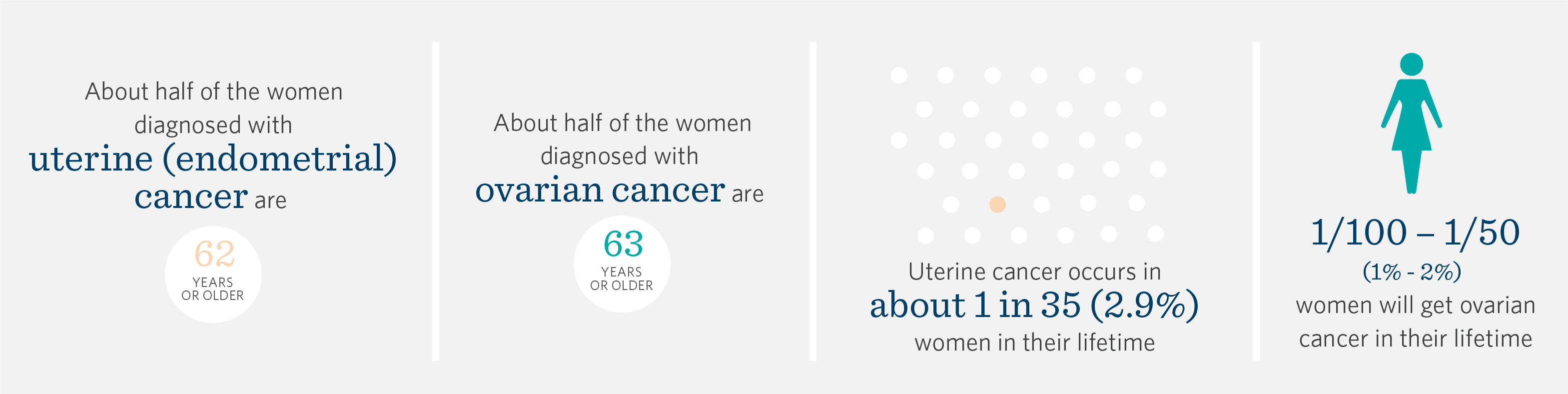
Types of Cancer

About Hereditary Cancer
Many people have a family history of cancer, but only 5-10% of uterine cancer and up to 25% of ovarian cancer is hereditary.
People who have these gene mutations are born with them – they do not develop over time.
Learning if you have an inherited mutation can help you know more about your cancer risks.
People with a higher chance of developing cancer may need screening, like mammograms, that start at younger ages, and occur more often.
Should You Have Genetic Testing?
If you answer “yes” to any of the questions below, hereditary gynecologic cancer genetic testing may be something for you and/or your
family members to consider.
|
1
|
Have you/your family members* been diagnosed with ovarian cancer? |
|
2
|
Have you/your family members* been diagnosed with uterine cancer <50 years old? |
|
3
|
Have you/your family members* been diagnosed with more than one cancer, such as uterine and colorectal cancer? |
|
4
|
Have multiple people on the same side of your family had ovarian, uterine, breast and/or other cancers? |
|
5
|
Have any of your family members* been found to have a cancer gene mutation? |
Your healthcare provider may identify other reasons why you could consider genetic testing.
* ”Family members” refers to blood relatives, such as brothers/sisters/parents/grandparents/aunts/uncles/cousins
What are the Benefits of Genetic Testing?
For You:
Your healthcare provider can adjust your cancer screening plan (such as age of initial screening, type, and frequency) based on your genetic test results.
- Examples of cancer screening include mammogram, breast MRI, colonoscopy, and dermatology exam
Your healthcare provider may discuss possible cancer prevention options, such as preventive surgery to reduce the risk for certain cancers.
- Examples are prophylactic mastectomy (removing one or both breasts before a cancer occurs) or prophylactic oophorectomy (removing the ovaries and Fallopian tubes before a cancer occurs)
Your doctor may discuss the possibility of other personalized treatment options based on your genetic test results.
for your family members:
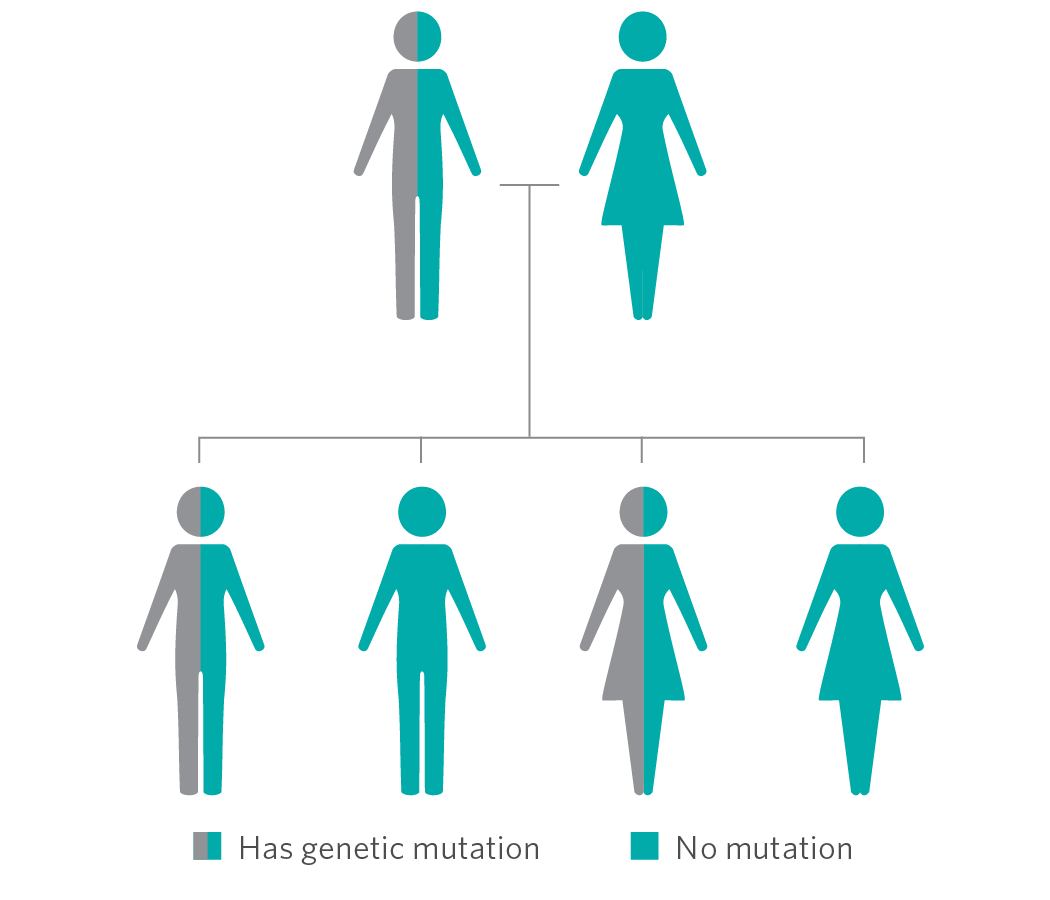
If you test positive for a genetic mutation, your close family members (like your parents, brothers, sisters, children) have a 50/50 random chance of also having the same mutation.
- Men and women have the same chance to inherit a mutation, but their chance to develop cancer may be different.
- Typically genetic testing is recommended for adults, but it is important to discuss genetic testing for children under age 18 with your healthcare provider to determine if it may be helpful.
Possible Genetic Test Results
Positive
A mutation was found in at least one of the genes tested
There are increased risks for cancer and may be management recommendations specific to the gene that has a mutation Genetic testing for certain family members may be recommended
Negative
No genetic changes were found in any of the genes tested
Cancer risk(s) and management recommendations are based on personal and family history Talk to your healthcare provider to find out if genetic testing should be considered for your family members
variant of unknown significance (vus)
At least one genetic change was found, but it is unclear if this change causes an increased risk for cancer or not
Cancer risk(s) and management recommendations are based on personal and family history Talk to your healthcare provider to find out if genetic testing should be considered for your family members
It is possible to have a combination of positive and VUS results, since multiple genes are tested.