Hereditary Heart Conditions
More than 1 in 60 people have an inherited cardiovascular condition
What is an Inherited Heart Condition?
There are many different conditions of the heart. Some are more likely to run in families. Inherited heart conditions are caused by a change or mutation in one gene or in a number of genes.
Types of inherited heart conditions include cardiomyopathies, arrhythmias, thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, and familial hypercholesterolemia. One of the most important reasons for identifying your risk early for a hereditary heart condition is because many of these conditions are often asymptomatic, and sudden death can be the first and only symptom.

More than 1 in 60 people have an inherited heart condition

There is a 50% chance of inheriting an autosomal dominant cardiovascular condition from an affected first-degree relative
Recognize the Symptoms of an Inherited Cardiovascular Condition
Most inherited heart conditions are passed down in an autosomal dominant chromosome pattern and often show up in multiple generations in a family. These conditions can also be associated with death at a young age due to sudden cardiac arrest or aortic dissection. Knowing whether you or a loved one are at an increased risk for one of these disorders can help make sure that proper medical care is administered to prevent any serious events.

Symptoms vary from person to person, but inherited cardiovascular disorders can cause:
Shortness of Breath | Fatigue Chest Pain | Irregular Heartbeat | Fainting | Coughing | Nausea even Sudden Death in rare cases.
How Genetic Testing May Help
Confirm or rule out a suspected inherited heart condition or help determine your chance of developing or passing it on.

Confirm a diagnosis, particularly when clinical criteria are unclear or borderline

Choose a better medicine or other treatment method

Identify an inherited mutation following a sudden unexplained death with autopsy findings

Clarify risks to family members, including the inheritance pattern

Reduce future healthcare costs, resources, and anxiety for families
How Genetic Testing May Help Your Family
WHAT HAPPENS IF I TEST POSITIVE FOR A GENE MUTATION?
There is a 50/50 chance that each of your children, brothers, sisters, and parents also has this same mutation.
Your family members can now be tested for this mutation. Any family members who also carry the mutation are at increased risk to develop the cardiovascular condition and should consult a cardiologist.
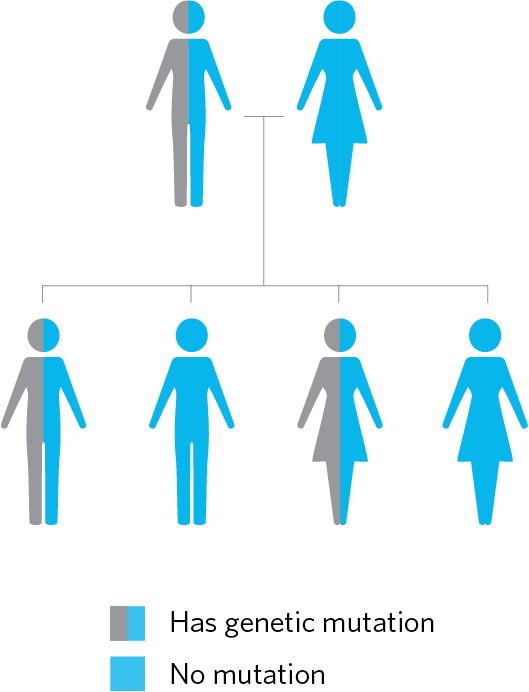
Any family members who test negative for this mutation are likely not at increased risk for the cardiovascular condition.
Am I a Candidate for Genetic Testing?
IF YOU ANSWER “YES” TO ANY OF THE QUESTIONS BELOW, HEREDITARY CARDIOVASCULAR GENETIC TESTING MAY BE SOMETHING FOR YOU AND/OR YOUR FAMILY MEMBERS TO CONSIDER.
Have you/your family members* been diagnosed with any inherited heart condition/disorder?
Have you/your family members* been diagnosed with high cholesterol?
Is there any history of a sudden unexpected death or cardiac arrest in your family?
Does anybody in your family have a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) device?
Is there a personal or family history of unexplained fainting or passing out?
If your responses indicate that you may be at-risk for a hereditary cardiovascular condition, there’s no need to panic.
Not everyone who has a risk will necessarily go on to develop disease. Genetic test results are a tool to help clarify your risk for cardiovascular conditions, and inform your healthcare provider in determining the best plan of action moving forward.
*Your healthcare provider may identify other reasons why it may be beneficial for you to consider genetic testing

What Test Results Can I Expect? And What Do I Do Once I Have Them?
POSITIVE, NEGATIVE, OR A VARIANT OF UNKNOWN SIGNIFICANCE (VUS)
Results from your genetic tests will fall into one of three categories:
A mutation related to a hereditary cardiovascular condition has been found in at least one of your tested genes:
A mutation was found in at least one of the genes tested.
There may be management recommendations specific to the gene that has a mutation.
Genetic testing for certain family members may be recommended.
No cardiovascular disease-related genetic mutations were found in any of your tested genes
Since inherited disease risk(s) and management recommendations are based on personal and family history as well as genetics, you may still want to discuss next steps with your healthcare provider.
Despite your negative result, genetic testing may be advisable for family members if they have been diagnosed with or are showing symptoms of cardiovascular disease.
At least one genetic mutation was found, but it is unclear if this change causes an increased risk for an inherited cardiovascular disease
Consult with your healthcare provider on if genetic testing should be considered for your family members. Recommendations vary based on personal and family history
These results may change over time as we learn more information and you could possibly get an updated result in the future
Tests and Gene Information
Find information about our cardiology tests here. Click the arrows to expand the gene list to see all of genes that are included on each test. By clicking on each gene, you can find more information that would be important for a person who tests positive for a mutation in that gene. These Understanding Your Results pages are included with positive test reports from Ambry.
LongQTNext™
A multi gene panel to identify and diagnose common inherited arrhythmias such as long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and short QT syndrome. The test can be an effective way to confirm an arrhythmia disorder and direct medical management and treatment decisions.
|
AKAP9 |
ANK2 |
CACNA1C |
CALM1 |
CALM2 |
CALM3 |
CAV3 |
KCNE1 |
|
KCNE2 |
KCNH2 |
KCNJ2 |
KCNJ5 |
KCNQ1 |
SCN4B |
SCN5A |
SNTA1 |
|
TRDN |
RhythmNext™
A multi gene panel to identify and diagnose common inherited arrhythmias such as long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and short QT syndrome. The test can be an effective way to confirm an arrhythmia disorder and direct medical management and treatment decisions.
|
AKAP9 |
ANK2 |
CACNA1C |
CACNA2D1 |
CACNB2 |
CALM1 |
CALM2 |
CALM3 |
|
CASQ2 |
CAV3 |
DES |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
DSP |
GPD1L |
HCN4 |
|
JUP |
KCND3 |
KCNE1 |
KCNE2 |
KCNE3 |
KCNH2 |
KCNJ2 |
KCNJ5 |
|
KCNJ8 |
KCNQ1 |
LMNA |
NKX2-5 |
PKP2 |
PLN |
RYR2 |
SCN10A |
|
SCN1B |
SCN3B |
SCN4B |
SCN5A |
SNTA1 |
TBX5 |
TECRL |
TMEM43 |
|
TRDN |
TRPM4 |
CPVTNext®
A 4 gene panel to identify catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, an inherited arrhythmia that occurs during the stress of exercise or an onset of emotion.
ARVCNext™
An 11 gene panel that identifies arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, an inherited disorder characterized by abnormal fat deposits around the wall of the heart. This can cause problems with the electrical system in the heart that controls the heartbeat’s regular rhythm.
|
DES |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
DSP |
JUP |
LMNA |
PKP2 |
PLN |
|
RYR2 |
SCN5A |
TMEM43 |
HCMNext®
A multi-gene panel that can identify at-risk individuals or confirm a diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), an enlarged heart muscle disease. Often, HCM can be asymptomatic and sudden death is the first and only symptom.
|
ACTC1 |
ACTN2 |
ALPK3 |
ANKRD1 |
CSRP3 |
FHL1 |
FLNC |
GLA |
|
JPH2 |
LAMP2 |
MYBPC3 |
MYH6 |
MYH7 |
MYL2 |
MYL3 |
MYPN |
|
NEXN |
PLN |
PRKAG2 |
PTPN11 |
RAF1 |
RIT1 |
SOS1 |
TCAP |
|
TNNC1 |
TNNI3 |
TNNT2 |
TPM1 |
TTR |
VCL |
DCMNext®
A 37 gene panel that identifies dilated cardiomyopathy, a disease characterized by enlargment of the heart’s left ventricle. This can cause problems with the electrical system in the heart that controls the heartbeat’s regular rhythm.
|
ABCC9 |
ACTC1 |
ACTN2 |
ALMS1 |
ANKRD1 |
BAG3 |
CSRP3 |
DES |
|
DMD |
DOLK |
DSP |
FKRP |
FLNC |
LAMA4 |
LAMP2 |
LDB3 |
|
LMNA |
MYBPC3 |
MYH6 |
MYH7 |
MYPN |
NEXN |
NKX2-5 |
PLN |
|
RAF1 |
RBM20 |
SCN5A |
TAZ |
TBX20 |
TCAP |
TNNC1 |
TNNI3 |
|
TNNT2 |
TPM1 |
TTN |
TTR |
VCL |
CMNext®
A multi gene panel that can identify many inherited cardiomyopathies. The 56 gene test can confirm a diagnosis and identify at-risk individuals, allowing for effective treatment and prevention management for the patient and their family.
|
ABCC9 |
ACTC1 |
ACTN2 |
ALMS1 |
ALPK3 |
ANKRD1 |
BAG3 |
CRYAB |
|
CSRP3 |
DES |
DMD |
DOLK |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
DSP |
EMD |
|
FHL1 |
FKRP |
FLNC |
GLA |
HCN4 |
JPH2 |
JUP |
LAMA4 |
|
LAMP2 |
LDB3 |
LMNA |
MYBPC3 |
MYH6 |
MYH7 |
MYL2 |
MYL3 |
|
MYPN |
NEXN |
NKX2-5 |
PKP2 |
PLN |
PRKAG2 |
PTPN11 |
RAF1 |
|
RBM20 |
RIT1 |
RYR2 |
SCN5A |
SOS1 |
TAZ |
TBX20 |
TCAP |
|
TMEM43 |
TNNC1 |
TNNI3 |
TNNT2 |
TPM1 |
TTN |
TTR |
VCL |
ARVCNext™
An 11 gene panel that identifies arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, an inherited disorder characterized by abnormal fat deposits around the wall of the heart. This can cause problems with the electrical system in the heart that controls the heartbeat’s regular rhythm.
|
DES |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
DSP |
JUP |
LMNA |
PKP2 |
PLN |
|
RYR2 |
SCN5A |
TMEM43 |
TAADNext®
A next generation sequencing panel that analyzes 35 genes associated with thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, Marfan syndrome and related disorders that often contribute to sudden cardiac death. The test can confirm a diagnosis and aid in patient management and treatment options.
|
ACTA2 |
BGN |
CBS |
CHST14 |
COL1A1 |
COL1A2 |
COL3A1 |
COL5A1 |
|
COL5A2 |
EFEMP2 |
FBN1 |
FBN2 |
FKBP14 |
FLNA |
FOXE3 |
LOX |
|
MAT2A |
MED12 |
MFAP5 |
MYH11 |
MYLK |
NOTCH1 |
PLOD1 |
PRDM5 |
|
PRKG1 |
SKI |
SLC2A10 |
SMAD3 |
SMAD4 |
TGFB2 |
TGFB3 |
TGFBR1 |
|
TGFBR2 |
TNXB |
ZNF469 |
CustomNext-Cardio®
A customizable panel of up to 167 genes that cause inherited cardiovascular or lipid disorders.
|
ABCA1 |
ABCC9 |
ABCG5 |
ABCG8 |
ACTA2 |
ACTC1 |
ACTN2 |
ACVRL1 |
|
AKAP9 |
ALMS1 |
ALPK3 |
ANK2 |
ANKRD1 |
APOA1 |
APOA5 |
APOB |
|
APOC2 |
APOC3 |
APOE |
BAG3 |
BGN |
BRAF |
CACNA1C |
CACNA2D1 |
|
CACNB2 |
CALM1 |
CALM2 |
CALM3 |
CASQ2 |
CAV3 |
CBL |
CBS |
|
CHST14 |
COL1A1 |
COL1A2 |
COL3A1 |
COL5A1 |
COL5A2 |
CRYAB |
CSRP3 |
|
CYP27A1 |
DES |
DMD |
DOLK |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
DSP |
EFEMP2 |
|
EMD |
ENG |
EPHB4 |
EYA4 |
FBN1 |
FBN2 |
FHL1 |
FKBP14 |
|
FKRP |
FKTN |
FLNA |
FLNC |
FOXE3 |
GAA |
GATA4 |
GATAD1 |
|
GDF2 |
GLA |
GPD1L |
GPIHBP1 |
HCN4 |
HRAS |
JAG1 |
JPH2 |
|
JUP |
KCND3 |
KCNE1 |
KCNE2 |
KCNE3 |
KCNH2 |
KCNJ2 |
KCNJ5 |
|
KCNJ8 |
KCNQ1 |
KRAS |
LAMA4 |
LAMP2 |
LCAT |
LDB3 |
LDLR |
|
LDLRAP1 |
LIPA |
LMF1 |
LMNA |
LOX |
LPL |
LZTR1 |
MAP2K1 |
|
MAP2K2 |
MAT2A |
MED12 |
MFAP5 |
MYBPC3 |
MYH11 |
MYH6 |
MYH7 |
|
MYL2 |
MYL3 |
MYLK |
MYOZ2 |
MYPN |
NEXN |
NF1 |
NKX2-5 |
|
NOTCH1 |
NRAS |
PCSK9 |
PKP2 |
PLN |
PLOD1 |
PPP1CB |
PRDM5 |
|
PRKAG2 |
PRKG1 |
PTPN11 |
RAF1 |
RASA1 |
RBM20 |
RIT1 |
RYR2 |
|
SCN10A |
SCN1B |
SCN2B |
SCN3B |
SCN4B |
SCN5A |
SHOC2 |
SKI |
|
SLC2A10 |
SLCO1B1 |
SMAD3 |
SMAD4 |
SNTA1 |
SOS1 |
SOS2 |
SPRED1 |
|
TAZ |
TBX1 |
TBX20 |
TBX5 |
TCAP |
TECRL |
TGFB2 |
TGFB3 |
|
TGFBR1 |
TGFBR2 |
TMEM43 |
TNNC1 |
TNNI3 |
TNNT2 |
TNXB |
TPM1 |
|
TRDN |
TRPM4 |
TTN |
TTR |
TXNRD2 |
VCL |
ZNF469 |
FHNext®
A next generation sequencing panel that analyzes 4 genes associated with familial hypercholesterolemia, a high cholesterol disorder. The test can help confirm a diagnosis and allow for individualized disease management and treatment.
CustomNext-Cardio®
A customizable panel of up to 167 genes that cause inherited cardiovascular or lipid disorders.
|
ABCA1 |
ABCC9 |
ABCG5 |
ABCG8 |
ACTA2 |
ACTC1 |
ACTN2 |
ACVRL1 |
|
AKAP9 |
ALMS1 |
ALPK3 |
ANK2 |
ANKRD1 |
APOA1 |
APOA5 |
APOB |
|
APOC2 |
APOC3 |
APOE |
BAG3 |
BGN |
BRAF |
CACNA1C |
CACNA2D1 |
|
CACNB2 |
CALM1 |
CALM2 |
CALM3 |
CASQ2 |
CAV3 |
CBL |
CBS |
|
CHST14 |
COL1A1 |
COL1A2 |
COL3A1 |
COL5A1 |
COL5A2 |
CRYAB |
CSRP3 |
|
CYP27A1 |
DES |
DMD |
DOLK |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
DSP |
EFEMP2 |
|
EMD |
ENG |
EPHB4 |
EYA4 |
FBN1 |
FBN2 |
FHL1 |
FKBP14 |
|
FKRP |
FKTN |
FLNA |
FLNC |
FOXE3 |
GAA |
GATA4 |
GATAD1 |
|
GDF2 |
GLA |
GPD1L |
GPIHBP1 |
HCN4 |
HRAS |
JAG1 |
JPH2 |
|
JUP |
KCND3 |
KCNE1 |
KCNE2 |
KCNE3 |
KCNH2 |
KCNJ2 |
KCNJ5 |
|
KCNJ8 |
KCNQ1 |
KRAS |
LAMA4 |
LAMP2 |
LCAT |
LDB3 |
LDLR |
|
LDLRAP1 |
LIPA |
LMF1 |
LMNA |
LOX |
LPL |
LZTR1 |
MAP2K1 |
|
MAP2K2 |
MAT2A |
MED12 |
MFAP5 |
MYBPC3 |
MYH11 |
MYH6 |
MYH7 |
|
MYL2 |
MYL3 |
MYLK |
MYOZ2 |
MYPN |
NEXN |
NF1 |
NKX2-5 |
|
NOTCH1 |
NRAS |
PCSK9 |
PKP2 |
PLN |
PLOD1 |
PPP1CB |
PRDM5 |
|
PRKAG2 |
PRKG1 |
PTPN11 |
RAF1 |
RASA1 |
RBM20 |
RIT1 |
RYR2 |
|
SCN10A |
SCN1B |
SCN2B |
SCN3B |
SCN4B |
SCN5A |
SHOC2 |
SKI |
|
SLC2A10 |
SLCO1B1 |
SMAD3 |
SMAD4 |
SNTA1 |
SOS1 |
SOS2 |
SPRED1 |
|
TAZ |
TBX1 |
TBX20 |
TBX5 |
TCAP |
TECRL |
TGFB2 |
TGFB3 |
|
TGFBR1 |
TGFBR2 |
TMEM43 |
TNNC1 |
TNNI3 |
TNNT2 |
TNXB |
TPM1 |
|
TRDN |
TRPM4 |
TTN |
TTR |
TXNRD2 |
VCL |
ZNF469 |
CardioNext®
An 92 gene panel that identifies inherited cardiomyopathies, inherited arrhythmias and other inherited cardiovascular conditions.
|
ABCC9 |
ACTC1 |
ACTN2 |
AKAP9 |
ALMS1 |
ALPK3 |
ANK2 |
ANKRD1 |
|
BAG3 |
CACNA1C |
CACNA2D1 |
CACNB2 |
CALM1 |
CALM2 |
CALM3 |
CASQ2 |
|
CAV3 |
CRYAB |
CSRP3 |
DES |
DMD |
DOLK |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
|
DSP |
EMD |
EYA4 |
FHL1 |
FKRP |
FKTN |
FLNC |
GATAD1 |
|
GLA |
GPD1L |
HCN4 |
JPH2 |
JUP |
KCND3 |
KCNE1 |
KCNE2 |
|
KCNE3 |
KCNH2 |
KCNJ2 |
KCNJ5 |
KCNJ8 |
KCNQ1 |
LAMA4 |
LAMP2 |
|
LDB3 |
LMNA |
MYBPC3 |
MYH6 |
MYH7 |
MYL2 |
MYL3 |
MYOZ2 |
|
MYPN |
NEXN |
NKX2-5 |
PKP2 |
PLN |
PRKAG2 |
PTPN11 |
RAF1 |
|
RBM20 |
RIT1 |
RYR2 |
SCN10A |
SCN1B |
SCN2B |
SCN3B |
SCN4B |
|
SCN5A |
SNTA1 |
SOS1 |
TAZ |
TBX20 |
TBX5 |
TCAP |
TECRL |
|
TGFB3 |
TMEM43 |
TNNC1 |
TNNI3 |
TNNT2 |
TPM1 |
TRDN |
TRPM4 |
|
TTN |
TTR |
TXNRD2 |
VCL |
CustomNext-Cardio®
A customizable panel of up to 167 genes that cause inherited cardiovascular or lipid disorders.
|
ABCA1 |
ABCC9 |
ABCG5 |
ABCG8 |
ACTA2 |
ACTC1 |
ACTN2 |
ACVRL1 |
|
AKAP9 |
ALMS1 |
ALPK3 |
ANK2 |
ANKRD1 |
APOA1 |
APOA5 |
APOB |
|
APOC2 |
APOC3 |
APOE |
BAG3 |
BGN |
BRAF |
CACNA1C |
CACNA2D1 |
|
CACNB2 |
CALM1 |
CALM2 |
CALM3 |
CASQ2 |
CAV3 |
CBL |
CBS |
|
CHST14 |
COL1A1 |
COL1A2 |
COL3A1 |
COL5A1 |
COL5A2 |
CRYAB |
CSRP3 |
|
CYP27A1 |
DES |
DMD |
DOLK |
DSC2 |
DSG2 |
DSP |
EFEMP2 |
|
EMD |
ENG |
EPHB4 |
EYA4 |
FBN1 |
FBN2 |
FHL1 |
FKBP14 |
|
FKRP |
FKTN |
FLNA |
FLNC |
FOXE3 |
GAA |
GATA4 |
GATAD1 |
|
GDF2 |
GLA |
GPD1L |
GPIHBP1 |
HCN4 |
HRAS |
JAG1 |
JPH2 |
|
JUP |
KCND3 |
KCNE1 |
KCNE2 |
KCNE3 |
KCNH2 |
KCNJ2 |
KCNJ5 |
|
KCNJ8 |
KCNQ1 |
KRAS |
LAMA4 |
LAMP2 |
LCAT |
LDB3 |
LDLR |
|
LDLRAP1 |
LIPA |
LMF1 |
LMNA |
LOX |
LPL |
LZTR1 |
MAP2K1 |
|
MAP2K2 |
MAT2A |
MED12 |
MFAP5 |
MYBPC3 |
MYH11 |
MYH6 |
MYH7 |
|
MYL2 |
MYL3 |
MYLK |
MYOZ2 |
MYPN |
NEXN |
NF1 |
NKX2-5 |
|
NOTCH1 |
NRAS |
PCSK9 |
PKP2 |
PLN |
PLOD1 |
PPP1CB |
PRDM5 |
|
PRKAG2 |
PRKG1 |
PTPN11 |
RAF1 |
RASA1 |
RBM20 |
RIT1 |
RYR2 |
|
SCN10A |
SCN1B |
SCN2B |
SCN3B |
SCN4B |
SCN5A |
SHOC2 |
SKI |
|
SLC2A10 |
SLCO1B1 |
SMAD3 |
SMAD4 |
SNTA1 |
SOS1 |
SOS2 |
SPRED1 |
|
TAZ |
TBX1 |
TBX20 |
TBX5 |
TCAP |
TECRL |
TGFB2 |
TGFB3 |
|
TGFBR1 |
TGFBR2 |
TMEM43 |
TNNC1 |
TNNI3 |
TNNT2 |
TNXB |
TPM1 |
|
TRDN |
TRPM4 |
TTN |
TTR |
TXNRD2 |
VCL |
ZNF469 |
FCSNext™
|
APOA5 |
APOC2 |
GPIHBP1 |
LMF1 |
LPL |
Sitosterolemia
|
ABCG5 |
ABCG8 |
NoonanNext™
|
BRAF |
CBL |
HRAS |
KRAS |
LZTR1 |
MAP2K1 |
MAP2K2 |
NF1 |
|
NRAS |
PPP1CB |
PTPN11 |
RAF1 |
RASA1 |
RIT1 |
SHOC2 |
SOS1 |
|
SOS2 |
SPRED1 |
Transthyretin amyloidosis
A genetic test that identifies transthyretin amyloidosis, a slowly progressive condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal deposits of a protein in the body’s organs and tissues. This buildup can cause loss of sensation in the extremities.
PCDNext®
A genetic test that identifies primary ciliary dyskinesia, a disorder that causes defects in the action of cilia lining the respiratory tract.
|
ARMC4 |
CCDC103 |
CCDC114 |
CCDC39 |
CCDC40 |
CFTR |
DNAAF1 |
DNAAF2 |
|
DNAAF3 |
DNAAF5 |
DNAH11 |
DNAH5 |
DNAI1 |
DNAI2 |
LRRC6 |
NME8 |
|
OFD1 |
RPGR |
RSPH4A |
RSPH9 |
SPAG1 |
Tests and Gene Information
Click on the disease or category below to see all genes that appear on the test.
-
Arrhythmia
-
LongQTNext™
A multi gene panel to identify and diagnose common inherited arrhythmias such as long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and short QT syndrome. The test can be an effective way to confirm an arrhythmia disorder and direct medical management and treatment decisions.
Gene List
AKAP9, ANK2, CACNA1C, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, CAV3, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNH2, KCNJ2, KCNJ5, KCNQ1, SCN4B, SCN5A, SNTA1, TRDN
-
RhythmNext™
A multi gene panel to identify and diagnose common inherited arrhythmias such as long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and short QT syndrome. The test can be an effective way to confirm an arrhythmia disorder and direct medical management and treatment decisions.
Gene List
AKAP9, ANK2, CACNA1C, CACNA2D1, CACNB2, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, CASQ2, CAV3, DES, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, GPD1L, HCN4, JUP, KCND3, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNE3, KCNH2, KCNJ2, KCNJ5, KCNJ8, KCNQ1, LMNA, NKX2-5, PKP2, PLN, RYR2, SCN10A, SCN1B, SCN3B, SCN4B, SCN5A, SNTA1, TBX5, TECRL, TMEM43, TRDN, TRPM4
-
CPVTNext®
A 4 gene panel to identify catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, an inherited arrhythmia that occurs during the stress of exercise or an onset of emotion.
Gene List
CALM1, CASQ2, RYR2, TRDN
-
ARVCNext™
An 11 gene panel that identifies arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, an inherited disorder characterized by abnormal fat deposits around the wall of the heart. This can cause problems with the electrical system in the heart that controls the heartbeat’s regular rhythm.
Gene List
DES, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, JUP, LMNA, PKP2, PLN, RYR2, SCN5A, TMEM43
-
-
Cardiomyopathy
-
HCMNext®
A multi-gene panel that can identify at-risk individuals or confirm a diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), an enlarged heart muscle disease. Often, HCM can be asymptomatic and sudden death is the first and only symptom.
Gene List
ACTC1, ACTN2, ALPK3, ANKRD1, CSRP3, FHL1, FLNC, GLA, JPH2, LAMP2, MYBPC3, MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYPN, NEXN, PLN, PRKAG2, PTPN11, RAF1, RIT1, SOS1, TCAP, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TPM1, TTR, VCL
-
DCMNext®
A 37 gene panel that identifies dilated cardiomyopathy, a disease characterized by enlargment of the heart’s left ventricle. This can cause problems with the electrical system in the heart that controls the heartbeat’s regular rhythm.
Gene List
ABCC9, ACTC1, ACTN2, ALMS1, ANKRD1, BAG3, CSRP3, DES, DMD, DOLK, DSP, FKRP, FLNC, LAMA4, LAMP2, LDB3, LMNA, MYBPC3, MYH6, MYH7, MYPN, NEXN, NKX2-5, PLN, RAF1, RBM20, SCN5A, TAZ, TBX20, TCAP, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TPM1, TTN, TTR, VCL
-
CMNext®
A multi gene panel that can identify many inherited cardiomyopathies. The 56 gene test can confirm a diagnosis and identify at-risk individuals, allowing for effective treatment and prevention management for the patient and their family.
Gene List
ABCC9, ACTC1, ACTN2, ALMS1, ALPK3, ANKRD1, BAG3, CRYAB, CSRP3, DES, DMD, DOLK, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, EMD, FHL1, FKRP, FLNC, GLA, HCN4, JPH2, JUP, LAMA4, LAMP2, LDB3, LMNA, MYBPC3, MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYPN, NEXN, NKX2-5, PKP2, PLN, PRKAG2, PTPN11, RAF1, RBM20, RIT1, RYR2, SCN5A, SOS1, TAZ, TBX20, TCAP, TMEM43, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TPM1, TTN, TTR, VCL
-
ARVCNext™
An 11 gene panel that identifies arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, an inherited disorder characterized by abnormal fat deposits around the wall of the heart. This can cause problems with the electrical system in the heart that controls the heartbeat’s regular rhythm.
Gene List
DES, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, JUP, LMNA, PKP2, PLN, RYR2, SCN5A, TMEM43
-
-
Aortic Aneurysms / Dissections
-
TAADNext®
A next generation sequencing panel that analyzes 35 genes associated with thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, Marfan syndrome and related disorders that often contribute to sudden cardiac death. The test can confirm a diagnosis and aid in patient management and treatment options.
Gene List
ACTA2, BGN, CBS, CHST14, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, EFEMP2, FBN1, FBN2, FKBP14, FLNA, FOXE3, LOX, MAT2A, MED12, MFAP5, MYH11, MYLK, NOTCH1, PLOD1, PRDM5, PRKG1, SKI, SLC2A10, SMAD3, SMAD4, TGFB2, TGFB3, TGFBR1, TGFBR2, TNXB, ZNF469
-
CustomNext-Cardio®
A customizable panel of up to 167 genes that cause inherited cardiovascular or lipid disorders.
Gene List
ABCA1, ABCC9, ABCG5, ABCG8, ACTA2, ACTC1, ACTN2, ACVRL1, AKAP9, ALMS1, ALPK3, ANK2, ANKRD1, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC2, APOC3, APOE, BAG3, BGN, BRAF, CACNA1C, CACNA2D1, CACNB2, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, CASQ2, CAV3, CBL, CBS, CHST14, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, CRYAB, CSRP3, CYP27A1, DES, DMD, DOLK, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, EFEMP2, EMD, ENG, EPHB4, EYA4, FBN1, FBN2, FHL1, FKBP14, FKRP, FKTN, FLNA, FLNC, FOXE3, GAA, GATA4, GATAD1, GDF2, GLA, GPD1L, GPIHBP1, HCN4, HRAS, JAG1, JPH2, JUP, KCND3, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNE3, KCNH2, KCNJ2, KCNJ5, KCNJ8, KCNQ1, KRAS, LAMA4, LAMP2, LCAT, LDB3, LDLR, LDLRAP1, LIPA, LMF1, LMNA, LOX, LPL, LZTR1, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAT2A, MED12, MFAP5, MYBPC3, MYH11, MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYLK, MYOZ2, MYPN, NEXN, NF1, NKX2-5, NOTCH1, NRAS, PCSK9, PKP2, PLN, PLOD1, PPP1CB, PRDM5, PRKAG2, PRKG1, PTPN11, RAF1, RASA1, RBM20, RIT1, RYR2, SCN10A, SCN1B, SCN2B, SCN3B, SCN4B, SCN5A, SHOC2, SKI, SLC2A10, SLCO1B1, SMAD3, SMAD4, SNTA1, SOS1, SOS2, SPRED1, TAZ, TBX1, TBX20, TBX5, TCAP, TECRL, TGFB2, TGFB3, TGFBR1, TGFBR2, TMEM43, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TNXB, TPM1, TRDN, TRPM4, TTN, TTR, TXNRD2, VCL, ZNF469
-
-
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
-
FHNext®
A next generation sequencing panel that analyzes 4 genes associated with familial hypercholesterolemia, a high cholesterol disorder. The test can help confirm a diagnosis and allow for individualized disease management and treatment.
Gene List
APOB, LDLR, LDLRAP1, PCSK9
-
CustomNext-Cardio®
A customizable panel of up to 167 genes that cause inherited cardiovascular or lipid disorders.
Gene List
ABCA1, ABCC9, ABCG5, ABCG8, ACTA2, ACTC1, ACTN2, ACVRL1, AKAP9, ALMS1, ALPK3, ANK2, ANKRD1, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC2, APOC3, APOE, BAG3, BGN, BRAF, CACNA1C, CACNA2D1, CACNB2, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, CASQ2, CAV3, CBL, CBS, CHST14, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, CRYAB, CSRP3, CYP27A1, DES, DMD, DOLK, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, EFEMP2, EMD, ENG, EPHB4, EYA4, FBN1, FBN2, FHL1, FKBP14, FKRP, FKTN, FLNA, FLNC, FOXE3, GAA, GATA4, GATAD1, GDF2, GLA, GPD1L, GPIHBP1, HCN4, HRAS, JAG1, JPH2, JUP, KCND3, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNE3, KCNH2, KCNJ2, KCNJ5, KCNJ8, KCNQ1, KRAS, LAMA4, LAMP2, LCAT, LDB3, LDLR, LDLRAP1, LIPA, LMF1, LMNA, LOX, LPL, LZTR1, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAT2A, MED12, MFAP5, MYBPC3, MYH11, MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYLK, MYOZ2, MYPN, NEXN, NF1, NKX2-5, NOTCH1, NRAS, PCSK9, PKP2, PLN, PLOD1, PPP1CB, PRDM5, PRKAG2, PRKG1, PTPN11, RAF1, RASA1, RBM20, RIT1, RYR2, SCN10A, SCN1B, SCN2B, SCN3B, SCN4B, SCN5A, SHOC2, SKI, SLC2A10, SLCO1B1, SMAD3, SMAD4, SNTA1, SOS1, SOS2, SPRED1, TAZ, TBX1, TBX20, TBX5, TCAP, TECRL, TGFB2, TGFB3, TGFBR1, TGFBR2, TMEM43, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TNXB, TPM1, TRDN, TRPM4, TTN, TTR, TXNRD2, VCL, ZNF469
-
-
Comprehensive Testing
-
CardioNext®
An 92 gene panel that identifies inherited cardiomyopathies, inherited arrhythmias and other inherited cardiovascular conditions.
Gene List
ABCC9, ACTC1, ACTN2, AKAP9, ALMS1, ALPK3, ANK2, ANKRD1, BAG3, CACNA1C, CACNA2D1, CACNB2, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, CASQ2, CAV3, CRYAB, CSRP3, DES, DMD, DOLK, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, EMD, EYA4, FHL1, FKRP, FKTN, FLNC, GATAD1, GLA, GPD1L, HCN4, JPH2, JUP, KCND3, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNE3, KCNH2, KCNJ2, KCNJ5, KCNJ8, KCNQ1, LAMA4, LAMP2, LDB3, LMNA, MYBPC3, MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYOZ2, MYPN, NEXN, NKX2-5, PKP2, PLN, PRKAG2, PTPN11, RAF1, RBM20, RIT1, RYR2, SCN10A, SCN1B, SCN2B, SCN3B, SCN4B, SCN5A, SNTA1, SOS1, TAZ, TBX20, TBX5, TCAP, TECRL, TGFB3, TMEM43, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TPM1, TRDN, TRPM4, TTN, TTR, TXNRD2, VCL
-
CustomNext-Cardio®
A customizable panel of up to 167 genes that cause inherited cardiovascular or lipid disorders.
Gene List
ABCA1, ABCC9, ABCG5, ABCG8, ACTA2, ACTC1, ACTN2, ACVRL1, AKAP9, ALMS1, ALPK3, ANK2, ANKRD1, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC2, APOC3, APOE, BAG3, BGN, BRAF, CACNA1C, CACNA2D1, CACNB2, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, CASQ2, CAV3, CBL, CBS, CHST14, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, CRYAB, CSRP3, CYP27A1, DES, DMD, DOLK, DSC2, DSG2, DSP, EFEMP2, EMD, ENG, EPHB4, EYA4, FBN1, FBN2, FHL1, FKBP14, FKRP, FKTN, FLNA, FLNC, FOXE3, GAA, GATA4, GATAD1, GDF2, GLA, GPD1L, GPIHBP1, HCN4, HRAS, JAG1, JPH2, JUP, KCND3, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNE3, KCNH2, KCNJ2, KCNJ5, KCNJ8, KCNQ1, KRAS, LAMA4, LAMP2, LCAT, LDB3, LDLR, LDLRAP1, LIPA, LMF1, LMNA, LOX, LPL, LZTR1, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAT2A, MED12, MFAP5, MYBPC3, MYH11, MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYLK, MYOZ2, MYPN, NEXN, NF1, NKX2-5, NOTCH1, NRAS, PCSK9, PKP2, PLN, PLOD1, PPP1CB, PRDM5, PRKAG2, PRKG1, PTPN11, RAF1, RASA1, RBM20, RIT1, RYR2, SCN10A, SCN1B, SCN2B, SCN3B, SCN4B, SCN5A, SHOC2, SKI, SLC2A10, SLCO1B1, SMAD3, SMAD4, SNTA1, SOS1, SOS2, SPRED1, TAZ, TBX1, TBX20, TBX5, TCAP, TECRL, TGFB2, TGFB3, TGFBR1, TGFBR2, TMEM43, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TNXB, TPM1, TRDN, TRPM4, TTN, TTR, TXNRD2, VCL, ZNF469
-
-
Other Lipid Disorders
-
FCSNext™
Gene List
APOA5, APOC2, GPIHBP1, LMF1, LPL
-
Sitosterolemia
Gene List
ABCG5, ABCG8
-
-
Noonan Syndrome / RASopathies
-
NoonanNext™
Gene List
BRAF, CBL, HRAS, KRAS, LZTR1, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, NF1, NRAS, PPP1CB, PTPN11, RAF1, RASA1, RIT1, SHOC2, SOS1, SOS2, SPRED1
-
-
Other
-
Transthyretin amyloidosis
A genetic test that identifies transthyretin amyloidosis, a slowly progressive condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal deposits of a protein in the body’s organs and tissues. This buildup can cause loss of sensation in the extremities.
Gene List
TTR
-
PCDNext®
A genetic test that identifies primary ciliary dyskinesia, a disorder that causes defects in the action of cilia lining the respiratory tract.
Gene List
ARMC4, CCDC103, CCDC114, CCDC39, CCDC40, CFTR, DNAAF1, DNAAF2, DNAAF3, DNAAF5, DNAH11, DNAH5, DNAI1, DNAI2, LRRC6, NME8, OFD1, RPGR, RSPH4A, RSPH9, SPAG1
-
Want to Know More About Genetic Testing?
Ambry’s current menu of genetic tests is focused in four categories of genetic disease: Hereditary Cancer, Heart Conditions, Hereditary Neurological Disorders, and Other Rare Conditions. If the condition you are concerned about falls into one of these categories, click on the appropriate button to learn more.